CyberShake Workflows
CyberShake relies on scientific workflows to provide the reliability, robustness, and automation needed to reach the necessary computational scale.
If we view the desired CyberShake PSHA hazard map calculation as a "problem", then we want to define the solution to this problem as a scientific workflow.
Software developed is based on using appropriate level of simplification (abstraction) to simplify how we specify the calculation. Progressed from assembly language (over op-codes), funcational programming (e.g. C), object-oriented (e.g. information hiding), relational database models (e.g. normal forms).
In our view, scientific workflows represent the appropriate level of abstraction in which we can define the solution to the CyberShake calculation on HPC systems.
Characteristics of Workflow Systems
We expect any workflow system to provide the following capabilities:
- Format for expressing program execution order and data dependencies.
- Job scheduler that automates the orderly execution of the programs.
- File and metadata management to track files in system.
- Support for distributed processing across multiple computing resources.
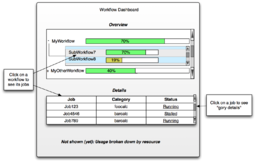
CyberShake Workflow Monitoring Dashboard
Prototype monitoring workflow.