CME Project
Contents
Community Modeling Environment (CME)
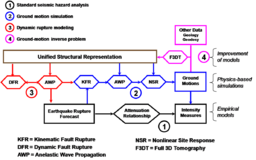
The SCEC Community Modeling Environment (SCEC/CME) Project [1] started in 2001 as a National Science Foundation (NSF) Information Technology Research (ITR) award to PI: Thomas H. Jordan, co-PIs: Bernard Minster, Carl Kesselman, and Reagan Moore. The CME collaboration applies advanced computer science technology to develop improved seismic hazard analysis. CME researchers develop structural models of California faults and geology, develop and validate rupture physics models, perform large-scale regional wave propagation simulations, collaborate with engineers studying engineering response to ground motions, and integrate computational improvements into probabilistic seismic hazard calculations.
Current project activities are posted on the SCECpedia home page at:
CME Project Reference
[1] Jordan, T.H., and P. Maechling (2003) The SCEC community modeling environment; An information infrastructure for system-level earthquake science, Seismol. Res. Lett., 74, 324-328.
CME Research Support
Southern California Earthquake Center (SCEC) and SCEC/CME research is funded by National Science Foundation (NSF) Cooperative Agreements EAR-0106924 and USGS Cooperative Agreement 02HQAG0008, and NSF awards EAR- 074493, EAR-0949443, OCI-0832698, and OCI-0832698. This research is supported by an allocation of advanced computing resources provided by the National Science Foundation (NSF). Computations are performed at San Diego Supercomputer Center, and the Texas Advanced Computing Center (TACC) at The University of Texas at Austin, the National Center for Supercomputer Applications (NCSA) provide HPC resources. Computations are supported by the University of Southern California Center for Center for High-Performance Computing (HPC). Our research uses HPC resources provided by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) through an Innovative and Novel Computational Impact on Theory and Experiment (INCITE) program allocation award. An award of computer time was provided by the INCITE program. This research uses resources of the Argonne Leadership Computing Facility at Argonne National Laboratory, which is supported by the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy under contract DE-AC02- 06CH11357. This research also used resources of the Oak Ridge Leadership Computing Facility, which is a DOE Office of Science User Facility supported under Contract DE-AC05-00OR22725.
See Also
Additional information about SCEC earthquake system science research is available on related SCEC web sites including:
License
Except as otherwise noted, SCEC material posted on this wiki is distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license and the SCEC software is distributed with Open Source Licenses, including the Apache 2.0 License and 3 Clause BSD license. For related information, see our Site Policies.
![]()