Difference between revisions of "UCVMC How to process bin data"
From SCECpedia
Jump to navigationJump to search| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
== metadata file == | == metadata file == | ||
| − | + | Metadata file contains many fields. Some of the fields are specific to the type | |
| − | of the plot that were made. | + | of the plot that were made. These are the fields for a horizontal slice plot. |
| − | |||
lon_list | lon_list | ||
| Line 37: | Line 36: | ||
(lon1,lat1) is the lower left corner of the plot and (lon2,lat2) is the upper right | (lon1,lat1) is the lower left corner of the plot and (lon2,lat2) is the upper right | ||
| − | corner of the plot. lon_list and lat_list are the | + | corner of the plot. lon_list and lat_list are the tick values of the axes. |
[http://hypocenter.usc.edu/research/UCVM/cvmh_no_ely_gtl/cvmh_nogtl_vs_0_map_meta.json metadata in json] | [http://hypocenter.usc.edu/research/UCVM/cvmh_no_ely_gtl/cvmh_nogtl_vs_0_map_meta.json metadata in json] | ||
Latest revision as of 19:21, 5 July 2018
Binary data can be generated from UCVMC's plotting tool in python or by one of the UCVMC app that is written to work with the UCVMC api.
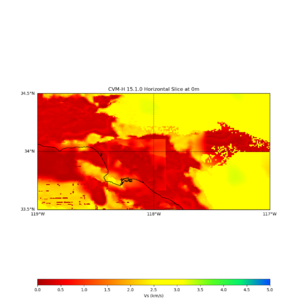
example plot
This is horizontal Vs slice plot from UCVMC's plot_horizontal_slice.py
metadata file
Metadata file contains many fields. Some of the fields are specific to the type of the plot that were made. These are the fields for a horizontal slice plot.
lon_list lat_list lat1 lon1 lat2 lon2 datafile num_x num_y min max color data_type outfile cvm_selected datapoints depth
(lon1,lat1) is the lower left corner of the plot and (lon2,lat2) is the upper right corner of the plot. lon_list and lat_list are the tick values of the axes.
binary data file
The data is written out as an array of float32. It can be imported with numpy in python,
import numpy as np
fh = open(rawfile, 'r')
floats = np.fromfile(fh, dtype=np.float32)
and fill into the 2D array as,
datapoints = np.arange(num_x * num_y,dtype=np.float32).reshape(num_y, num_x)
i=0
j=0
for f in floats:
datapoints[i][j] = f
j = j + 1
if j >= num_x:
j = 0
i = i + 1