Difference between revisions of "UCERF3"
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
[[File:Ucerf3p2 M6 5.jpg|200px|thumb|left]] | [[File:Ucerf3p2 M6 5.jpg|200px|thumb|left]] | ||
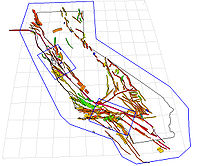
| − | Figure 1: This map shows the Uniform California Earthquake Rupture Forecast v.3 (UCERF3) which forecasts the probability of all possible damaging earthquakes greater than magnitude 5 throughout California over a given time frame such as the next 30 years. This map view of California shows active California faults as defined in UCERF3. The fault colors show the UCERF3 forecast of the rate at which each fault section will participate in an earthquake rupture with magnitude greater than 6.5. Less likely sections are shown in blue and more likely sections in red. | + | Figure 1: This map shows the Uniform California Earthquake Rupture Forecast v.3 (UCERF3) which forecasts the probability of all possible damaging earthquakes greater than magnitude 5.0 throughout California over a given time frame such as the next 30 years. This map view of California shows active California faults as defined in UCERF3. The fault colors show the UCERF3 forecast of the rate at which each fault section will participate in an earthquake rupture with magnitude greater than 6.5. Less likely sections are shown in blue and more likely sections in red. |
The light blue boundary identifies the UCERF model region, which comprises California and a buffer zone. The blue boxes highlight the San Francisco Bay Area and Los Angeles Regions. | The light blue boundary identifies the UCERF model region, which comprises California and a buffer zone. The blue boxes highlight the San Francisco Bay Area and Los Angeles Regions. | ||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
(Image Credit: Kevin Milner University of Southern California) | (Image Credit: Kevin Milner University of Southern California) | ||
| − | |||
== UCERF 3 Fault and Background Seismicity Participation Rates== | == UCERF 3 Fault and Background Seismicity Participation Rates== | ||
Revision as of 19:36, 6 March 2013
UCERF 3 Fault Participation Rates
Figure 1: This map shows the Uniform California Earthquake Rupture Forecast v.3 (UCERF3) which forecasts the probability of all possible damaging earthquakes greater than magnitude 5.0 throughout California over a given time frame such as the next 30 years. This map view of California shows active California faults as defined in UCERF3. The fault colors show the UCERF3 forecast of the rate at which each fault section will participate in an earthquake rupture with magnitude greater than 6.5. Less likely sections are shown in blue and more likely sections in red.
The light blue boundary identifies the UCERF model region, which comprises California and a buffer zone. The blue boxes highlight the San Francisco Bay Area and Los Angeles Regions.
SCEC scientists used TACC supercomputers Ranger and Stampede to calculate the hazards from many alternative earthquake rupture scenarios and to combine the results in the final UCERF3 earthquake rupture forecast.
(Image Credit: Kevin Milner University of Southern California)
UCERF 3 Fault and Background Seismicity Participation Rates
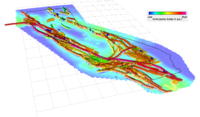
Figure 2: This map shows the Uniform California Earthquake Rupture Forecast v.3 (UCERF3) which forecasts the probability of all possible damaging earthquakes greater than magnitude 5 throughout California over a given time frame such as the next 5 years. This map view of California shows active California faults as defined in UCERF3. The fault colors show the UCERF3 forecast of the rate at which each fault section will participate in an earthquake rupture with magnitude greater than 6.7. Less likely sections are shown in blue and more likely sections in red. The background colors on the map show UCERF3 earthquake rate forecasts for off-fault regions.
SCEC scientists used TACC supercomputers including Ranger and Stampede to calculate the hazards from many alternative earthquake rupture scenarios and to combine the results into the final UCERF3 earthquake rupture forecast.
(Image Credit: Kevin Milner University of Southern California)