Difference between revisions of "CyberShake Study 2.3"
(→SBSM) |
(Redirected page to CyberShake Study 13.4) |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | #redirect [[CyberShake Study 13.4]] | ||
CyberShake Study 2.3 is a proposed study to calculate hazard curves under [[CyberShake 1.5]] using CVM-S and CVM-H with the RWG V3.0.3 SGT code and AWP-ODC-SGT, and the Graves and Pitarka (2010) rupture variations. The goal is to calculate the same Southern California site list (286 sites) as for past CyberShake studies so we can produce comparison curves and maps, and understand the impact of the SGT codes and velocity models on the CyberShake seismic hazard. | CyberShake Study 2.3 is a proposed study to calculate hazard curves under [[CyberShake 1.5]] using CVM-S and CVM-H with the RWG V3.0.3 SGT code and AWP-ODC-SGT, and the Graves and Pitarka (2010) rupture variations. The goal is to calculate the same Southern California site list (286 sites) as for past CyberShake studies so we can produce comparison curves and maps, and understand the impact of the SGT codes and velocity models on the CyberShake seismic hazard. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *[[CyberShake Study 13.4]] | ||
== Proposed sites == | == Proposed sites == | ||
| Line 104: | Line 107: | ||
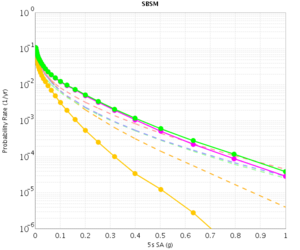
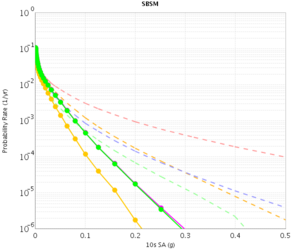
=== SBSM === | === SBSM === | ||
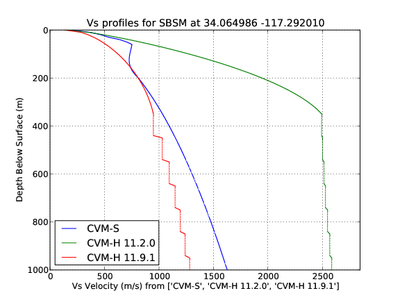
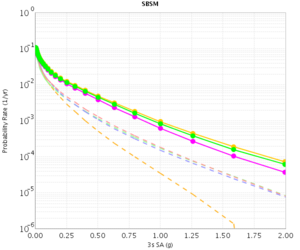
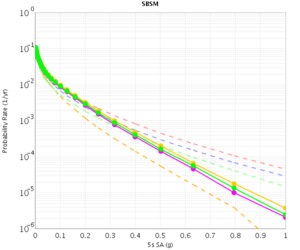
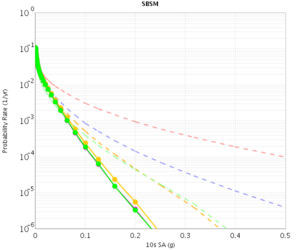
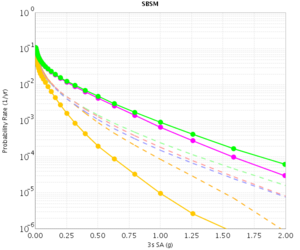
| − | The CVM-H curves are quite different for RWG V3.0.3 and RWG V3. This is because the V3 curves were made with CVM-H 11.2, whereas the RWG V3.0.3 (and AWP) curves were made with CVM-H 11.9. The update in CVM-H included the addition of the San Bernardino basin, which makes a big impact. | + | The CVM-H curves are quite different for RWG V3.0.3 and RWG V3. This is because the V3 curves were made with CVM-H 11.2, whereas the RWG V3.0.3 (and AWP) curves were made with CVM-H 11.9. The update in CVM-H included the addition of the San Bernardino basin, which makes a big impact. You can see this on a velocity profile at SBSM: |
| + | |||
| + | [[File:SBSM_velocity_profile.png|400px]] | ||
{| | {| | ||
| Line 122: | Line 127: | ||
| [[File:SBSM_CVM-H_RWGvAWP_10s.png|thumb|300px|RWG V3.0.3 (green), AWP (purple), RWG V3 (orange)]] | | [[File:SBSM_CVM-H_RWGvAWP_10s.png|thumb|300px|RWG V3.0.3 (green), AWP (purple), RWG V3 (orange)]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Papers and Presentations == | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://hypocenter.usc.edu/research/cybershake/Study_13_4_Science_Readiness_Review.pptx Science Readiness Review] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://hypocenter.usc.edu/research/cybershake/Study_13_4_Technical_Readiness_Review.pptx Technical Readiness Review] | ||
== Related Entries == | == Related Entries == | ||
*[[Geoinformatics Project]] | *[[Geoinformatics Project]] | ||
*[[SEISM Project]] | *[[SEISM Project]] | ||
Latest revision as of 00:32, 11 April 2013
Redirect to:
CyberShake Study 2.3 is a proposed study to calculate hazard curves under CyberShake 1.5 using CVM-S and CVM-H with the RWG V3.0.3 SGT code and AWP-ODC-SGT, and the Graves and Pitarka (2010) rupture variations. The goal is to calculate the same Southern California site list (286 sites) as for past CyberShake studies so we can produce comparison curves and maps, and understand the impact of the SGT codes and velocity models on the CyberShake seismic hazard.
Contents
Proposed sites
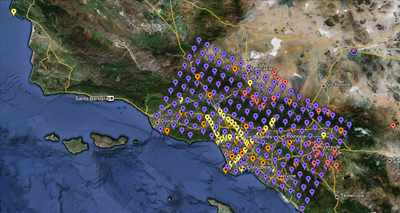
We are proposing to run 286 sites around Southern California. Those sites include 46 points of interest, 27 precarious rock sites, 23 broadband station locations, 43 20 km gridded sites, and 147 10 km gridded sites. All of them fall within the Southern California box except for Diablo Canyon and Pioneer Town. You can get a CSV file listing the sites here. A KML file listing the sites is available here.
Computational and Data Estimates
We are planning to use Blue Waters, Stampede, and Kraken for this calculation. We plan to calculate 286 sets of 2-component SGTs for each of RWG CVM-S, RWG CVM-H, AWP CVM-S, AWP CVM-H for a total of 1144 sets of SGTs.
We estimate the following requirements for each system. Data estimates are for generated data we may want to keep (SGTs, seismograms, PSA).
Blue Waters
Use for SGT calculations
572 sets of AWP SGTs x 5000 SUs/set = 2.9M SUs 572 sets of RWG SGTs x 5500 SUs/set = 3.2M SUs Total: 6.1M SUs 1144 sets of SGTs x 40 GB/set = 44.7 TB
Stampede
Use for RWG post-processing and half of AWP
858 sites x 900 SUs/site = 850k SUs 858 sites x 11.6 GB/site = 9.7 TB output data (seismograms, spectral acceleration)
Kraken
Use for half of AWP post-processing
286 sites x 5500 SUs/site = 1.6M SUs 286 sites x 11.6 GB/site = 3.2 TB output data (seismograms, spectral acceleration)
SCEC storage
1144 sites x 11.6 GB/site = 13.0 TB stored output data 1144 sites x 4.9 GB/site = 5.5 TB workflow logs
Verification
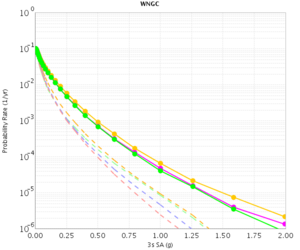
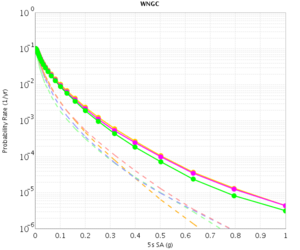
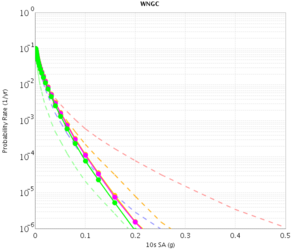
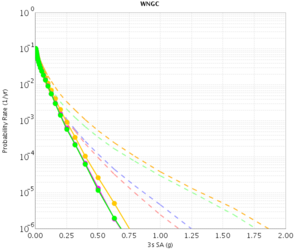
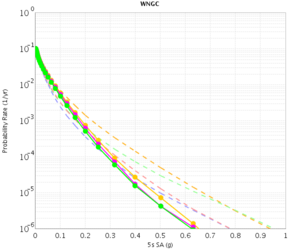
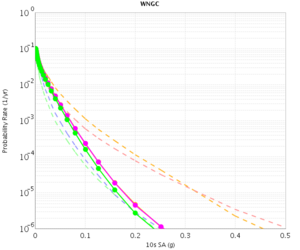
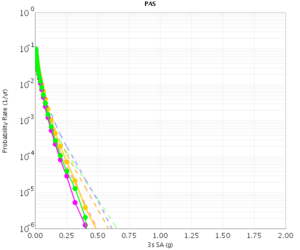
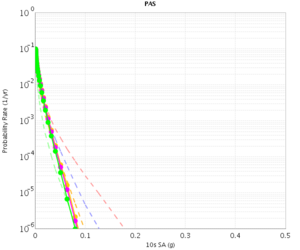
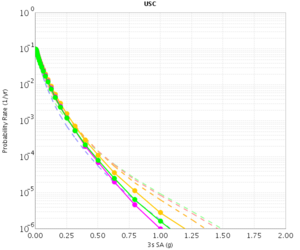
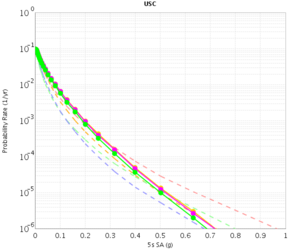
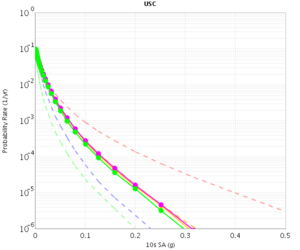
Before beginning Study 2.3 production runs, we first generated hazard curves in all 4 conditions (RWG CVM-S, RWG CVM-H, AWP CVM-S, AWP CVM-H) for 4 test sites, WNGC, PAS, USC, and SBSM. Below are hazard curves comparing these results, along with the previous version of RWG (V3).
WNGC
| 3s | 5s | 10s | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CVM-S | |||
| CVM-H |
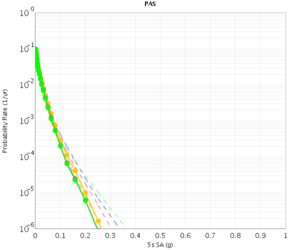
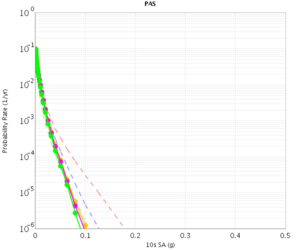
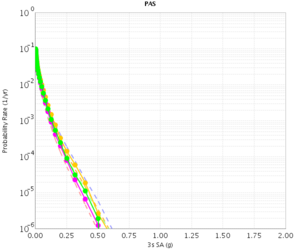
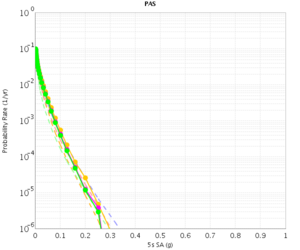
PAS
| 3s | 5s | 10s | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CVM-S | |||
| CVM-H |
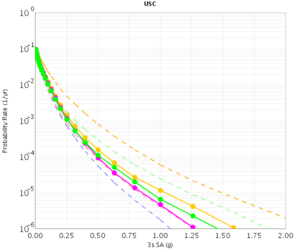
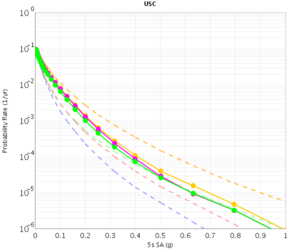
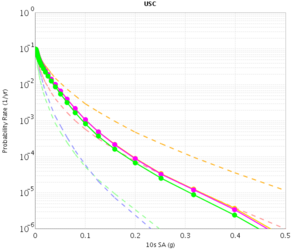
USC
| 3s | 5s | 10s | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CVM-S | |||
| CVM-H |
SBSM
The CVM-H curves are quite different for RWG V3.0.3 and RWG V3. This is because the V3 curves were made with CVM-H 11.2, whereas the RWG V3.0.3 (and AWP) curves were made with CVM-H 11.9. The update in CVM-H included the addition of the San Bernardino basin, which makes a big impact. You can see this on a velocity profile at SBSM:
| 3s | 5s | 10s | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CVM-S | |||
| CVM-H |