Difference between revisions of "UCVM API"
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
query multiple velocity models in a program. The API currently support these models: | query multiple velocity models in a program. The API currently support these models: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Crustal Models: | ||
* [[CVM-S]] | * [[CVM-S]] | ||
* [[CVM-H]] | * [[CVM-H]] | ||
| Line 11: | Line 13: | ||
* Rob Graves Cape Mendocino | * Rob Graves Cape Mendocino | ||
* Any user-defined model that can be encapsulated in a C header and source/library file | * Any user-defined model that can be encapsulated in a C header and source/library file | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | GTL Models: | ||
| + | * Ely Vs30-derived GTL | ||
| + | |||
Notes: | Notes: | ||
* MPI-capable, has been shown to scale to 2100 cores on NCCS Jaguar in a mesh generator. | * MPI-capable, has been shown to scale to 2100 cores on NCCS Jaguar in a mesh generator. | ||
| − | * Allows application programs to tailor which set of | + | * Allows application programs to tailor which set of velocity models are linked in to minimize memory footprint. |
* API is currently a prototype C interface. | * API is currently a prototype C interface. | ||
* Compatible with grid resources that have data stage-in policies for jobs, such as USC HPCC, and light-weight kernels that support static libraries only, such as NCCS Jaguar and NICS Kraken. | * Compatible with grid resources that have data stage-in policies for jobs, such as USC HPCC, and light-weight kernels that support static libraries only, such as NCCS Jaguar and NICS Kraken. | ||
| − | * Tested on NCCS Jaguar and USC HPCC. | + | * Tested on NCCS Jaguar, NICS Kraken, and USC HPCC. |
| + | |||
Significant science issues remain to be resolved. Please see the Science Issues section below. | Significant science issues remain to be resolved. Please see the Science Issues section below. | ||
| − | == | + | = Interface = |
| + | |||
| + | == UCVM Interface == | ||
| − | + | UCVM provides an interface for querying Vp, Vs, and rho from any user-defined model. Models are referenced either by a pre-defined string id or by a populated <code>ucvm_model_t</code> structure. Pre-defined models include CVM-S, CVM-H, CenCal, Lin-Thurber, Rob Graves Cape Mendocino, 1D, and Ely GTL. These models may be enabled by calling <code>ucvm_add_model()</code> with their string identifier as listed in ucvm_dtypes.h. | |
| + | Main UCVM interface: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| − | /* | + | #ifndef UCVM_H |
| − | + | #define UCVM_H | |
| + | |||
| + | #include <stdarg.h> | ||
| + | #include "ucvm_dtypes.h" | ||
| + | |||
| + | /* Initializer */ | ||
| + | int ucvm_init(const char *config); | ||
| + | |||
| + | /* Finalizer */ | ||
| + | int ucvm_finalize(); | ||
| + | |||
| + | /* Enable specific model, by label or by ucvm_model_t */ | ||
| + | int ucvm_add_model(const char *label); | ||
| + | int ucvm_add_user_model(ucvm_model_t *m); | ||
| + | |||
| + | /* Associate specific interp func with GTL model, by label | ||
| + | or by ucvm_ifunc_t */ | ||
| + | int ucvm_assoc_ifunc(const char *mlabel, const char *ilabel); | ||
| + | int ucvm_assoc_user_ifunc(const char *mlabel, ucvm_ifunc_t *ifunc); | ||
| + | |||
| + | /* Get label for a model */ | ||
| + | int ucvm_model_label(int m, char *label, int len); | ||
| + | |||
| + | /* Get label for an interpolation function */ | ||
| + | int ucvm_ifunc_label(int f, char *label, int len); | ||
| − | /* | + | /* Get version for a model */ |
| − | + | int ucvm_model_version(int m, char *ver, int len); | |
| − | /* | + | /* Set parameters (see ucvm_dtypes.h for valid param flags) */ |
| − | + | int ucvm_setparam(ucvm_param_t param, ...); | |
| + | |||
| + | /* Query underlying models */ | ||
| + | int ucvm_query(int n, ucvm_point_t *pnt, ucvm_data_t *data); | ||
| − | / | + | #endif |
| − | + | </pre> | |
| − | / | + | The programmer may also define their own models and integrate them into UCVM. A user model is defined by creating the init(), finalize(), version(), setparam(), and query() functions for the model, and populating the <code>ucvm_model_t</code> structure with these function pointers and some additional record keeping information. Once a model is fully described in a <code>ucvm_model_t</code>, it can be registered for use with the <code>ucvm_add_user_model()</code> function and queried with the <code>ucvm_query()</code> function. |
| − | |||
| − | + | Multiple models may be registered, and they are queried in order of registration. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | === Data Type Descriptions === | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | / | + | The full list of defined data types are listed in /include/ucvm_dtypes.h. The following is a general description of the useful application definitions: |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | Points are specified with a <code>ucvm_point_t</code> structure: | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
/* 3D point */ | /* 3D point */ | ||
typedef struct ucvm_point_t | typedef struct ucvm_point_t | ||
| Line 65: | Line 92: | ||
double coord[3]; | double coord[3]; | ||
} ucvm_point_t; | } ucvm_point_t; | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| − | / | + | |
| − | typedef struct | + | Return data is specified with a <code>ucvm_data_t</code> structure: |
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | typedef struct ucvm_data_t | ||
{ | { | ||
| − | + | double surf; /* Elevation of free surface in meters */ | |
| − | } | + | double vs30; /* Vs30 value in m/s */ |
| + | ucvm_prop_t crust; /* Material properties from crustal model */ | ||
| + | ucvm_prop_t gtl; /* Material properties from GTL model */ | ||
| + | ucvm_prop_t cmb; /* Combined GTL/crustal material properties. This is the final property set that applications should reference. */ | ||
| + | } ucvm_data_t; | ||
| + | |||
| + | where ucvm_prop_t is: | ||
/* Material properties */ | /* Material properties */ | ||
typedef struct ucvm_prop_t | typedef struct ucvm_prop_t | ||
{ | { | ||
| − | int | + | int source; /* Model idenfitifer */ |
| − | double vp; | + | double vp; /* Velocity in m/s */ |
| − | double vs; | + | double vs; /* Velocity in m/s */ |
| − | double rho; | + | double rho; /* Density in g/m^3 */ |
} ucvm_prop_t; | } ucvm_prop_t; | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | Models (both crustal and GTL) are specified with a <code>ucvm_model_t</code> structure: | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
/* Model */ | /* Model */ | ||
typedef struct ucvm_model_t | typedef struct ucvm_model_t | ||
{ | { | ||
char label[UCVM_MAX_LABEL_LEN]; | char label[UCVM_MAX_LABEL_LEN]; | ||
| + | ucvm_mtype_t mtype; | ||
ucvm_region_t region; | ucvm_region_t region; | ||
char config[UCVM_MAX_PATH_LEN]; | char config[UCVM_MAX_PATH_LEN]; | ||
| Line 113: | Line 131: | ||
int (*finalize)(); | int (*finalize)(); | ||
const char* (*version)(); | const char* (*version)(); | ||
| + | int (*setparam)(int param, ...); | ||
int (*query)(ucvm_ctype_t cmode, | int (*query)(ucvm_ctype_t cmode, | ||
int n, ucvm_point_t *pnt, | int n, ucvm_point_t *pnt, | ||
| − | + | ucvm_data_t *data); | |
} ucvm_model_t; | } ucvm_model_t; | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| Line 196: | Line 176: | ||
int nn = 1; | int nn = 1; | ||
ucvm_point_t pnt1; | ucvm_point_t pnt1; | ||
| − | + | ucvm_data_t data1; | |
printf("Init\n"); | printf("Init\n"); | ||
| Line 222: | Line 202: | ||
printf("Query Model\n"); | printf("Query Model\n"); | ||
| − | if (ucvm_query(nn, &pnt1, & | + | if (ucvm_query(nn, &pnt1, &data1) != UCVM_CODE_SUCCESS) { |
fprintf(stderr, "Query CVM failed\n"); | fprintf(stderr, "Query CVM failed\n"); | ||
return(1); | return(1); | ||
| Line 229: | Line 209: | ||
printf("Results\n"); | printf("Results\n"); | ||
printf("model=%d, vp=%lf, vs=%lf, rho=%lf\n", | printf("model=%d, vp=%lf, vs=%lf, rho=%lf\n", | ||
| − | + | data1.cmb.model, data1.cmb.vp, data1.cmb.vs, data1.cmb.rho); | |
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| Line 253: | Line 233: | ||
= Future Improvements = | = Future Improvements = | ||
| − | * | + | * Allow query by elevation |
* Addition of other regional models | * Addition of other regional models | ||
| − | * Addition of | + | * Addition of additional GTLs |
* Bindings for Fortran, C++ | * Bindings for Fortran, C++ | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 18:56, 4 May 2011
Contents
Overview
The Unified California Velocity Model API (UCVM API) is a programming interface that allows the user to directly query multiple velocity models in a program. The API currently support these models:
Crustal Models:
- CVM-S
- CVM-H
- USGS Central California
- Hadley-Kanamori 1D
- Lin Thurber CVM California Statewide
- Rob Graves Cape Mendocino
- Any user-defined model that can be encapsulated in a C header and source/library file
GTL Models:
- Ely Vs30-derived GTL
Notes:
- MPI-capable, has been shown to scale to 2100 cores on NCCS Jaguar in a mesh generator.
- Allows application programs to tailor which set of velocity models are linked in to minimize memory footprint.
- API is currently a prototype C interface.
- Compatible with grid resources that have data stage-in policies for jobs, such as USC HPCC, and light-weight kernels that support static libraries only, such as NCCS Jaguar and NICS Kraken.
- Tested on NCCS Jaguar, NICS Kraken, and USC HPCC.
Significant science issues remain to be resolved. Please see the Science Issues section below.
Interface
UCVM Interface
UCVM provides an interface for querying Vp, Vs, and rho from any user-defined model. Models are referenced either by a pre-defined string id or by a populated ucvm_model_t structure. Pre-defined models include CVM-S, CVM-H, CenCal, Lin-Thurber, Rob Graves Cape Mendocino, 1D, and Ely GTL. These models may be enabled by calling ucvm_add_model() with their string identifier as listed in ucvm_dtypes.h.
Main UCVM interface:
#ifndef UCVM_H #define UCVM_H #include <stdarg.h> #include "ucvm_dtypes.h" /* Initializer */ int ucvm_init(const char *config); /* Finalizer */ int ucvm_finalize(); /* Enable specific model, by label or by ucvm_model_t */ int ucvm_add_model(const char *label); int ucvm_add_user_model(ucvm_model_t *m); /* Associate specific interp func with GTL model, by label or by ucvm_ifunc_t */ int ucvm_assoc_ifunc(const char *mlabel, const char *ilabel); int ucvm_assoc_user_ifunc(const char *mlabel, ucvm_ifunc_t *ifunc); /* Get label for a model */ int ucvm_model_label(int m, char *label, int len); /* Get label for an interpolation function */ int ucvm_ifunc_label(int f, char *label, int len); /* Get version for a model */ int ucvm_model_version(int m, char *ver, int len); /* Set parameters (see ucvm_dtypes.h for valid param flags) */ int ucvm_setparam(ucvm_param_t param, ...); /* Query underlying models */ int ucvm_query(int n, ucvm_point_t *pnt, ucvm_data_t *data); #endif
The programmer may also define their own models and integrate them into UCVM. A user model is defined by creating the init(), finalize(), version(), setparam(), and query() functions for the model, and populating the ucvm_model_t structure with these function pointers and some additional record keeping information. Once a model is fully described in a ucvm_model_t, it can be registered for use with the ucvm_add_user_model() function and queried with the ucvm_query() function.
Multiple models may be registered, and they are queried in order of registration.
Data Type Descriptions
The full list of defined data types are listed in /include/ucvm_dtypes.h. The following is a general description of the useful application definitions:
Points are specified with a ucvm_point_t structure:
/* 3D point */
typedef struct ucvm_point_t
{
double coord[3];
} ucvm_point_t;
Return data is specified with a ucvm_data_t structure:
typedef struct ucvm_data_t
{
double surf; /* Elevation of free surface in meters */
double vs30; /* Vs30 value in m/s */
ucvm_prop_t crust; /* Material properties from crustal model */
ucvm_prop_t gtl; /* Material properties from GTL model */
ucvm_prop_t cmb; /* Combined GTL/crustal material properties. This is the final property set that applications should reference. */
} ucvm_data_t;
where ucvm_prop_t is:
/* Material properties */
typedef struct ucvm_prop_t
{
int source; /* Model idenfitifer */
double vp; /* Velocity in m/s */
double vs; /* Velocity in m/s */
double rho; /* Density in g/m^3 */
} ucvm_prop_t;
Models (both crustal and GTL) are specified with a ucvm_model_t structure:
/* Model */
typedef struct ucvm_model_t
{
char label[UCVM_MAX_LABEL_LEN];
ucvm_mtype_t mtype;
ucvm_region_t region;
char config[UCVM_MAX_PATH_LEN];
int (*init)(int id, ucvm_region_t *r, const char *config);
int (*finalize)();
const char* (*version)();
int (*setparam)(int param, ...);
int (*query)(ucvm_ctype_t cmode,
int n, ucvm_point_t *pnt,
ucvm_data_t *data);
} ucvm_model_t;
UCVM Grid Interface
Provides an interface for generating 2D regular grids in any USGS map projection.
/* Generate grid from projection and dimensions */
int ucvm_grid_gen(ucvm_proj_t *iproj, ucvm_trans_t *trans,
ucvm_proj_t *oproj,
ucvm_dim_t *dims, double spacing,
ucvm_point_t *pnts);
/* Generate grid from projection and dimensions */
int ucvm_grid_gen_file(ucvm_proj_t *iproj, ucvm_trans_t *trans,
ucvm_proj_t *oproj,
ucvm_dim_t *dims, double spacing,
const char *filename);
/* Convert point list from one projection to another */
int ucvm_grid_convert(ucvm_proj_t *iproj,
ucvm_proj_t *oproj,
size_t n, ucvm_point_t *pnts);
/* Convert point list from one projection to another */
int ucvm_grid_convert_file(ucvm_proj_t *iproj,
ucvm_proj_t *oproj,
size_t n, const char *filename);
Example Usage of API
The following code snippet illustrates how the API is used:
int nn = 1;
ucvm_point_t pnt1;
ucvm_data_t data1;
printf("Init\n");
if (ucvm_init("./ucvm.conf") != UCVM_CODE_SUCCESS) {
fprintf(stderr, "Init failed\n");
return(1);
}
printf("Query Mode\n");
if (ucvm_query_mode(UCVM_COORD_GEO_DEPTH) != UCVM_CODE_SUCCESS) {
fprintf(stderr, "Set query mode failed\n");
return(1);
}
printf("Add Model CVM-S\n");
if (ucvm_add_model(UCVM_MODEL_CVMS) != UCVM_CODE_SUCCESS) {
fprintf(stderr, "Retrieval of CVM-S failed\n");
return(1);
}
printf("Create point\n");
pnt1.coord[0] = -119.0;
pnt1.coord[1] = 31.0;
pnt1.coord[2] = 2000.0;
printf("Query Model\n");
if (ucvm_query(nn, &pnt1, &data1) != UCVM_CODE_SUCCESS) {
fprintf(stderr, "Query CVM failed\n");
return(1);
}
printf("Results\n");
printf("model=%d, vp=%lf, vs=%lf, rho=%lf\n",
data1.cmb.model, data1.cmb.vp, data1.cmb.vs, data1.cmb.rho);
Source Code
The UCVM source and cvm2mesh mesh generator may be checked out from SVN with these commands:
UCVM: svn co https://source.usc.edu/svn/ucvm/trunk
cvm2mesh: svn co https://source.usc.edu/svn/cvm2mesh/trunk
Implementation Details
- Models are queried in the order they are enabled in the interface. The material properties for a particular (lon,lat) point are from the first model in the ordered list to return valid values.
- Only lon,lat,dep coordinates are currently supported
- No smoothing between models is performed. They are simply tiled.
- Projections are performed with the Proj.4 package
- Depth is defined as the offset from the free surface (ground-air interface, ground-water interface) in meters, positive down. Negative depths are not supported.
Future Improvements
- Allow query by elevation
- Addition of other regional models
- Addition of additional GTLs
- Bindings for Fortran, C++
Science Issues
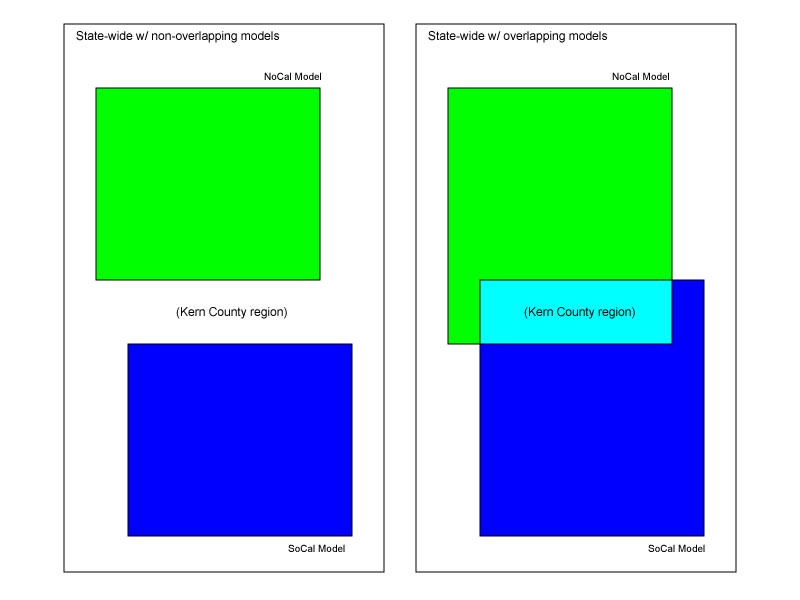
Overlapping Models
Imagine the scenario outlined below, where the user wishes to combine two models, a SoCal model and a NoCal model:
The models may overlap in ways which makes merging them difficult.
- For a point that falls within the Kern County region, simply interpolating between the two models may not work if NoCal reports water properties (vp, rho, no vs) and the SoCal model reports soil/rock. No interpolation is possible in this case. To deal with this situation, there are several options:
- Coordinate edits to each model to bring their material properties into better agreement within the overlap region.
- Crop one or both models to remove the overlap, and smooth them into the California background model.
- Create a new “Transition Model” that covers Kern County and surrounding area that interpolates/averages the the two other models in a scientifically acceptable way. Register this new model in the API, and give it priority over the other two models. In effect, tile the Transition Model, the NoCal Model, and the SoCal Model.
- Allow the models to overlap with discontinuities. This is currently how the UCVM API handles overlap.
Projection Distortion
Several issues with map projections come into play:
- Distortion in projections on large scales. Any state-wide model that supports querying by UTM or other projection coordinates must account for and minimize distortion.
- Inconsistent handling of projections within models. Each model generally has its own internal projection. For example, CVM-H uses a UTM projection. The projection codes used across all models should be standardized on the Proj.4 projection package to avoid small differences in the handling of coordinates. This may require resampling of the data inside the models.
Standardized Handling of Elevation
All models that support query by elevation should use a standard DEM derived from the same source.
GTL
If a state-wide GTL is developed, the GTL within each underlying model must be stripped away.