Difference between revisions of "Main Page"
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
*[http://scec.usc.edu/scecpedia/Special:PopularPages Most Popular Pages] | *[http://scec.usc.edu/scecpedia/Special:PopularPages Most Popular Pages] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Recent CME Wiki Entries == | == Recent CME Wiki Entries == | ||
| Line 90: | Line 86: | ||
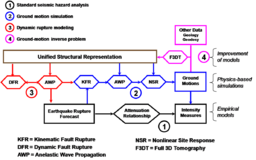
[[File:pathways.png|256px|thumb|right|Fig 1: SCEC/CME computational pathways provide a scientific framework for improving seismic ground motion forecasts. The SCEC/CME Project began as an NSF information technology research (ITR) project in 2001. (Image Credit: Thomas H. Jordan) ]] | [[File:pathways.png|256px|thumb|right|Fig 1: SCEC/CME computational pathways provide a scientific framework for improving seismic ground motion forecasts. The SCEC/CME Project began as an NSF information technology research (ITR) project in 2001. (Image Credit: Thomas H. Jordan) ]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Recent Earthquake Information == | ||
| + | An important goal of SCEC earthquake research is to reduce the hazard from future earthquakes by developing physics-based predictive models of earthquake processes. | ||
| + | *[http://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/recenteqscanv/ Recent California Earthquakes] | ||
| + | *[http://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/recenteqsww/ Recent Worldwide Earthquakes] | ||
== Overviews and Summaries == | == Overviews and Summaries == | ||
Revision as of 23:12, 29 July 2011
Contents
Community Modeling Environment (CME)
This is a collaborative wiki site for SCEC's Community Modeling Environment (CME). The CME is a collaborative, interdisciplinary research group that applies advanced computer science technology to the problem of seismic hazard analysis. This SCEC community wiki is configured to support our distributed research by providing a collection point for information about SCEC scientific computing research projects.
List of All SCECpedia Pages
The following link with take you to an alphabetically sorted list of all SCECpedia pages.
Recent CME Wiki Entries
The following list of SCECpedia topics are sorted chronologically with new and recently updated entries shown at the top of the list. This list of topics may not be complete, so we recommend you use the List of All SCECpedia Pages link if you want a comprehensive list of all entries.
- UCVM Workshop
- Broadband Platform
- UCVM
- PetaSHA2
- Earthquake Early Warning
- Transient Detection
- CyberShake
- ESP
- Early Science Program
- INCITE
- Open Science Grid
- M8
- Workflow Program Requirements
- Publications
- Goodness of Fit
- Standard Rupture Format
- OEF
- Software
- CME Project
- Full 3D Tomography
- SCEC Scientific Software Page
- SCEC Visualization Projects
- OpenSHA
- Wall to Wall
- SCEC Websims Simulation Data Access
- Computational Pathways
- Computational Platforms
- ANSS Catalog
- CSEP
- Petascale Computing
- Coulomb Failure Stress
- Earthquake Response
- Collaboration Tools
- Software Testing
- Software Documentation
- Contact Information
- ESRI
- Git
- SAC
- TeraShake
Meetings, Conferences
- SSA
- TeraGrid/Blue Waters Symposium on Data-Intensive Analysis, Analytics, and Informatics
- AGU
- CME Response - ShakeOut 10/21/10
Recent Earthquake Information
An important goal of SCEC earthquake research is to reduce the hazard from future earthquakes by developing physics-based predictive models of earthquake processes.
Overviews and Summaries
Types of SCEC/CME Web Sites
The SCEC/CME collaboratory provides three levels of access to web-based project information. The levels differ on who can read and edit information on the web site. Default Read access is public to facilitate collaboration. Project private web pages are provided if needed.
- Public SCEC Project Pages
- (Read Access: Public - Write Access: SCEC Communications Education and Outreach)
- SCECpedia Collaborative Wiki
- (Read Access: Public - Write Access: SCEC)
- SCEC Private Wiki
- (Read Access: SCEC - Write Access: SCEC)
CME Research Support
Southern California Earthquake Center (SCEC) and SCEC/CME research is funded by National Science Foundation (NSF) Cooperative Agreements EAR-0106924 and USGS Cooperative Agreement 02HQAG0008, and NSF awards EAR- 074493, EAR-0949443, OCI-0832698, and OCI-0832698. This research is supported by an allocation of advanced computing resources provided by the National Science Foundation (NSF). Computations are performed on Kraken (a Cray XT5) at the National Institute for Computational Sciences. Computations and data management are performed at San Diego Supercomputer Center, where the iRODS Data System is used. The Texas Advanced Computing Center (TACC) at The University of Texas at Austin, the National Center for Supercomputer Applications (NCSA) and the Pittsburgh Supercomputer Center (PSC) provide HPC resources. Computations are supported by the University of Southern California Center for High-Performance Computing and Communications (HPCC). Our research uses HPC resources provided by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) through an Innovative and Novel Computational Impact on Theory and Experiment (INCITE) program allocation award. Computations were performed on Jaguar, which is part of the National Center for Computational Science (NCCS) at the Oak Ridge National Laboratory which is supported by under DOE Contract No. DE-AC05-00OR22725. This research uses resources of the Argonne Leadership Computing Facility at Argonne National Laboratory, which is supported by the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy under contract DE-AC02- 06CH11357. The Ohio State University one-sided MPI Communication research was supported through NSF HECURA-1 (CCF- 0833169/139/155). This research received technical and user support through the Advanced Support for TeraGrid Applications (ASTA) program.
See Also
Additional information about SCEC earthquake system science research is available on related SCEC web sites including: